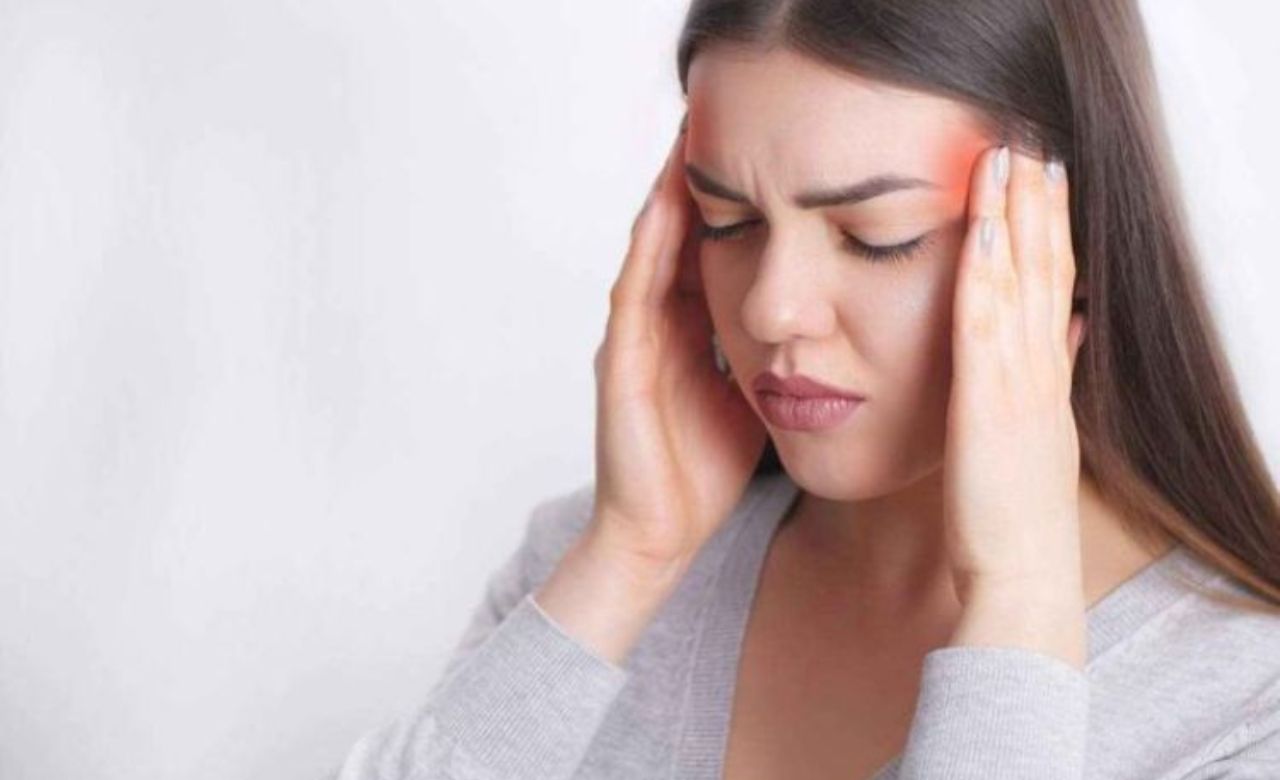
Migraine Headache is a neurological condition that occurs due to abnormal brain activity affecting nerve signals, chemicals and blood vessels in the brain. The pulsing pain generally occurs in the forehead, the side of the head, or around the eyes. The headache increasingly gets worse.
It is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, numbness, tingling, sensitivity to light and sound. Migraine attacks can last from 4-72 hours and the pain can be severe.
Migraine Symptoms
Migraines can begin in childhood, adolescence or early adulthood. It can undergo four stages but not for everyone: Prodrome, Aura, Attack and Post-drome.
Prodrome
Migraine symptoms which begin one or two days before the headache itself is known as Prodrome stage.
- Depression
- Food cravings
- Fatigue
- Yawning
- Hyperactivity
- Irritability
- Neck stiffness
Migraine with Aura
Migraine with Aura occurs after prodrome stage. During Aura, the patient may have problems with vision, sensation, movement and speech.
- Speaking difficulty
- Tingling sensation in face, arms or legs.
- Observing light flashes or bright spots.
- Temporary loss of vision.
- Hearing noises or music
- Uncontrollable jerking
Attack Phase
The most severe pain occurs in the attack phase due to Migraine.
- Sensitivity increase in light and sound.
- Nausea
- Feeling faint
- Pain on one side of head, either on left, right, front or back side of the temples.
- Pulsing head pain
- Vomiting
Postdrome Phase
During this phase, patients can change their moods and feelings such as euphoric, extremely happy, feeling very fatigued and apathetic. The phase length can vary in different degrees in different people. Sometimes, a phase may also be skipped.
Migraine Causes
The cause of migraine is not fully understood, but it is believed that genetics, changes in the brain and its interactions with the trigeminal nerve might be involved. Imbalances in the brain chemicals – Serotonin regulates pain in nervous system.
Emotional triggers
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Tension
- Shock
- Depression
- Excitement
Physical triggers
- Tiredness
- Poor-Quality Sleep
- Shift Work
- Poor Posture
- Neck or Shoulder Tension
- Jet Lag
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycaemia)
Diet triggers
- Missed, Delayed or Irregular Meals
- Dehydration
- Alcohol
- Caffeine Products such as Tea and Coffee
- Specific Foods such as Chocolate and Citrus fruit
- Foods Containing Tyramine
Environmental triggers
- Bright lights
- Flickering screens, such as a television or computer screen
- Smoking (or smoky rooms)
- Loud noises
- Strong smells
Medicational triggers
- Some types of sleeping tablets
- The combined contraceptive pill
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) used to relieve symptoms associated with menopause.
Types of Migraine
Migraine headaches are of different types. The most common are Classical Migraines and Common Migraines.
Classical Migraines
Classical migraines begin with a warning sign called Aura. The Aura often involves changes in flashing lights, colours or shadows and temporary loss of vision.
Common Migraines
Common Migraines doesn’t start with Aura and hence called as Migraines Without Aura. Common migraines may start slowly and interfere with daily activities. The pain of common migraines on only one side of your head. Most of the people are affected with common migraines only.
Chronic Migraine
Chronic migraine causes triggering attacks on over 15 days of the month.
Menstrual Migraine
Menstrual Migraine attacks occur in a pattern connected during the menstrual cycle.
Hemiplegic Migraine
Hemiplegic Migraine causes faintness on one side of the body for a temporary period.
Abdominal Migraine
Abdominal Migraine is a disorder that connects migraine attacks to irregular function in the gut and abdomen. It generally effects in children under 14 years of age.
Migraine with brainstem aura
This is a rare type of migraine that can cause severe neurological symptoms, such as affected speech.
Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are rare headaches that occur in patterns, known as cluster periods. Cluster headaches can be very painful. They generally cause pain on one side of your head.
Cervicogenic headaches
Cervicogenic headaches are caused by illness or physical condition, generally a problem in neck. Most of the time, this type of headache can occur by a sudden movement of neck. It occurs on one side of your head or face.
Retinal Migraine
A retinal migraine occurs due to temporary vision loss in one eye, which can last from minutes to months, but it is usually reversible. This is a more serious medical problem, and patients should seek medical care.
Vestibular migraine
Vestibular migraine is also known as migraine-associated vertigo. These symptoms affect balance and cause dizziness.
Acute migraine
Acute migraine is known as episodic migraine. People who suffer from episodic migraines have headaches up to 14 days a month.
Ayurveda Management for Migraine
Migraine treatment in Ayurveda is stated as Ardhavabedhaka that defines one-sided pain which is intense and piercing in nature. In Ayurveda, Migraine dominated with Vata-Pitta Dosha patient may have intense pain feel Redness and Burning sensation in the eyes. Generally, migraine is associated with the previous history of acidity, digestive issues.
Migraine Ayurveda treatment can be accomplished through the management of:
Samshodhana (Panchakarma-Bio-purificatory techniques)
- Kaya virechana (therapeutic purgation)
- Pathya ahara (regulated diet)
- Vihara (regulated lifestyle)
Shathayu Ayurveda has customized research and evidence-based treatments based on the severity of migraine. The Migraine Kit (combination of medications) is the best and safest way to treat migraine in 120 days along with diet & lifestyle modification without any side effects & complications.


1627984513.jpg)
1627984513.jpg)
1627984513.jpg)
%20(1)1627984512.jpg)


























1627984537.jpg)